2024
|
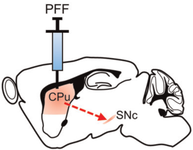
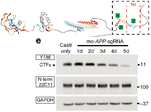
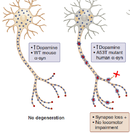
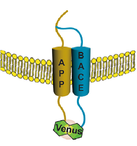
Long term rescue of Alzheimer’s deficits in vivo by one-time gene-editing of App C-terminus.
Brent D. Aulston, Kirstan Gimse, Hannah O. Bazick, Eniko A. Kramar, Donald P. Pizzo, Leonardo A. Parra-Rivas, Jichao Sun, Kristen Branes-Guerrero, Nidhi Checka, Neda Bagheri, Nihal Satyadev, Jared Carlson-Stevermer, Takashi Saito, Takaomi C. Saido, Anjon Audhya, Marcelo A. Wood, Mark J. Zylka, Krishanu Saha, and Subhojit Roy* https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2024.06.08.598099v1.full Alzforum coverage: www.alzforum.org/news/research-news/toward-ad-crispr-therapy-tweaking-app-terminus-cuts-plaque |
|
|
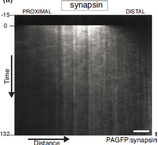
Spectrin condensates provide a nidus for assembling the periodic axonal structure
Nicholas P. Boyer, Rohan Sharma, Theresa Wiesner, Antoine Delamare, Florence Pelletier, Christophe Leterrier, Subhojit Roy. https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2024.06.05.597638v2.full |
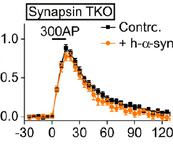
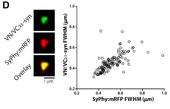
Synapsin E-domain is essential for alpha-synuclein function.
Alexandra Stavsky**, Leonardo A. Parra-Rivas**, Shani Tal, Kayalvizhi Madhivanan, Subhojit Roy* and Daniel Gitler*
(** co-first, * co-corresponding).
eLife: https://elifesciences.org/articles/89687
Alexandra Stavsky**, Leonardo A. Parra-Rivas**, Shani Tal, Kayalvizhi Madhivanan, Subhojit Roy* and Daniel Gitler*
(** co-first, * co-corresponding).
eLife: https://elifesciences.org/articles/89687
2023

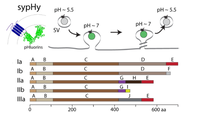
Serine-129 phosphorylation of α-synuclein is a trigger for physiologic protein-protein interactions and synaptic function.
Leonardo A. Parra-Rivas*, Kayalvizhi Madhivanan*, Brent D. Aulston, Lina Wang, Dube Dheeraj Prakashchand, Nicholas P. Boyer, Veronica M. Saia-Cerada, Kristen Branes-Guerrero, Donald P. Pizzo, Pritha Bagchi, V.S. Sundar, Yong Tang, Utpal Das, Utpal Das, David A. Scott, Padmini Rangamani, Yuki Ogawa, and Subhojit Roy
- Cover Article (open access): https://www.cell.com/neuron/fulltext/S0896-6273(23)00894-2
- Coverage by NIH News: Link
- Podcast in journal Neurology: https://directory.libsyn.com/episode/index/id/30066358
- Spotlight article, Trends in Biochemical Sciences: Link
- Alzforum news (of BioRxiv article): https://www.alzforum.org/news/research-news/not-all-bad-phosphorylated-synuclein-modulates-neurotransmission
BioRxiv: https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2022.12.22.521485www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2022.12.22.521485v1v1
Leonardo A. Parra-Rivas*, Kayalvizhi Madhivanan*, Brent D. Aulston, Lina Wang, Dube Dheeraj Prakashchand, Nicholas P. Boyer, Veronica M. Saia-Cerada, Kristen Branes-Guerrero, Donald P. Pizzo, Pritha Bagchi, V.S. Sundar, Yong Tang, Utpal Das, Utpal Das, David A. Scott, Padmini Rangamani, Yuki Ogawa, and Subhojit Roy
- Cover Article (open access): https://www.cell.com/neuron/fulltext/S0896-6273(23)00894-2
- Coverage by NIH News: Link
- Podcast in journal Neurology: https://directory.libsyn.com/episode/index/id/30066358
- Spotlight article, Trends in Biochemical Sciences: Link
- Alzforum news (of BioRxiv article): https://www.alzforum.org/news/research-news/not-all-bad-phosphorylated-synuclein-modulates-neurotransmission
BioRxiv: https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2022.12.22.521485www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2022.12.22.521485v1v1
Diminished Neuronal ESCRT-0 Function Exacerbates AMPA Receptor Derangement and Accelerates Prion-Induced Neurodegeneration. Lawrence JA, Aguilar-Calvo P, Ojeda-Juárez D, Khuu H, Soldau K, Pizzo DP, Wang J, Malik A, Shay TF, Sullivan EE, Aulston B, Song SM, Callender JA, Sanchez H, Geschwind MD, Roy S, Rissman RA, Trejo J, Tanaka N, Wu C, Chen X, Patrick GN, Sigurdson CJ.
J Neurosci. 2023. May 24;43(21):3970-3984. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1878-22.2023.
https://www.jneurosci.org/content/43/21/3970.abstract
J Neurosci. 2023. May 24;43(21):3970-3984. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1878-22.2023.
https://www.jneurosci.org/content/43/21/3970.abstract
2022
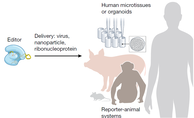
Efficient in vivo neuronal genome editing in the mouse brain using nanocapsules containing CRISPR-Cas9 ribonucleoproteins. Metzger JM, Wang Y, Neuman SS, Snow KJ, Murray SA, Lutz CM, Bondarenko V, Felton J, Gimse K, Xie R, Li D, Zhao Y, Flowers MT, Simmons HA, Roy S, Saha K,
Levine JE, Emborg ME, Gong S.
Biomaterials. 2023 Feb;293:121959. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2022.121959. Epub 2022 Dec 13. PMID: 36527789; PMCID: PMC9868115.
Levine JE, Emborg ME, Gong S.
Biomaterials. 2023 Feb;293:121959. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2022.121959. Epub 2022 Dec 13. PMID: 36527789; PMCID: PMC9868115.
Diminished neuronal ESCRT-0 function exacerbates AMPA receptor derangement and accelerates prion-induced neurodegeneration. Lawrence JA, Aguilar-Calvo P, Ojeda-Juárez D, Khuu H, Soldau K, Pizzo DP, Wang J, Malik A, Shay TF, Sullivan EE, Aulston B, Song SM, Callender JA, Sanchez H, Geschwind MD, Roy S, Rissman RA, Trejo J, Tanaka N, Wu C, Chen X, Patrick GN, Sigurdson CJ. J Neurosci. 2023 Apr 5:JN-RM-1878-22. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1878-22.2023. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 37019623.
2021
|
Dopamine neurons exhibit emergent glutamatergic identity in Parkinson's disease. Steinkellner T, Conrad WS, Kovacs I, Rissman RA, Lee EB, Trojanowski JQ, Freyberg Z, Roy S, Luk KC, Lee VM, Hnasko TS*. Brain. 2021 Nov 19:awab373. doi: 10.1093/brain/awab373. PMID: 35258081. Link: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35258081/ |
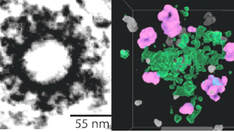
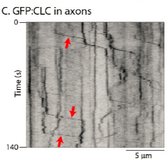
Clathrin packets move in slow axonal transport and deliver functional payloads to synapses.
Ganguly A**, Sharma, R**, Boyer, NP, Wernert F, Phan S, Boassa D, Das U, Caillol G, Han X, Yates JR, Ellisman MH, Leterrier C and Roy S*.
** co-first authors
Neuron, Sept 2021: https://www.cell.com/neuron/fulltext/S0896-6273(21)00613-9
Research highlighted in Nature Reviews in Neuroscience: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41583-021-00529-6
Ganguly A**, Sharma, R**, Boyer, NP, Wernert F, Phan S, Boassa D, Das U, Caillol G, Han X, Yates JR, Ellisman MH, Leterrier C and Roy S*.
** co-first authors
Neuron, Sept 2021: https://www.cell.com/neuron/fulltext/S0896-6273(21)00613-9
Research highlighted in Nature Reviews in Neuroscience: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41583-021-00529-6
Gene-based therapies for neurodegenerative diseases. Jichao Sun and Subhojit Roy (review) Nature Neuroscience, Feb 2021: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41593-020-00778-1 Open access (read only version) Podcast (RARECAST) on applying gene therapies to neurodegenerative diseases: globalgenes.org/rare-cast/episode-323/ |
|
|
The NIH Somatic Cell Genome Editing program.
Saha et al. (SCGE consortium) Nature, April 2021: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-021-03191-1 |
|
2020
|
Finding order in Slow Axonal Transport.
Roy S*. (Review, 2020). Current Opinion in Neurobiology, Read paper here (Editors Thomas Shwartz and Hollis Cline) |
|
Slow axonal transport and presynaptic targeting of clathrin packets. Ganguly A, Wernert F, Phan S, Boassa D, Das U, Sharma R, Caillol G, Han X, Yates JR, Ellisman MH, Leterrier C and Roy S*. (2020). Preprint at BioRxiv: https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.02.20.958140v2 |
|
2019 *corresponding author
|
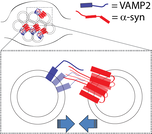
Sun J, Wang L, Bao H, Premi S, Das U, Chapman ER, Roy S*. Functional cooperation of α-synuclein and VAMP2 in synaptic vesicle recycling.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 May 20 <direct submission>. pii: 201903049. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1903049116. [Epub ahead of print] PubMed PMID: 31110017. https://www.pnas.org/content/early/2019/05/17/1903049116 (open access) |
|
|
Atias M, Tevet Y, Sun J, Stavsky A, Tal S, Kahn J, Roy S*, Gitler D*. Synapsins regulate α-synuclein functions.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 May 20 <direct submission>. pii: 201903054. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1903054116. [Epub ahead of print] PubMed PMID: 31110014. https://www.pnas.org/content/early/2019/05/16/1903054116 (open access) |
|
|
Proteomic Atlas of the Human Brain in Alzheimer's Disease.
McKetney J, Runde RM, Hebert AS, Salamat S, Roy S, Coon JJ*. J Proteome Res. 2019 Feb 20. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.9b00004. PubMed PMID: 30735395. Read paper here |
|
CRISPR/Cas9 editing of APP C-terminus attenuates β-cleavage and promotes α-cleavage.
Sun J, Carlson-Stevermer J, Das U, Shen M, Delenclos M, Snead AM, Koo SY, Wang L, Qiao D, Loi J, Petersen AJ, Stockton M, Bhattacharyya A, Jones MV, Zhao X, McLean PJ, Sproul AA, Saha K, Roy S*. Nature Communications. 2019 Jan 3;10(1):53. PMID: 30604771. Read paper here |
|
Processive flow by biased polymerization mediates the slow axonal transport of actin. Nilaj Chakrabarty, Pankaj Dubey, Yong Tang, Archan Ganguly, Kelsey Ladt, Christophe Leterrier*, Peter Jung*, Subhojit Roy*.
Journal of Cell Biology. 2019 Jan. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201711022.[Epub ahead of print] PubMed PMID: 30401699. Read paper here 2018 |
|
|
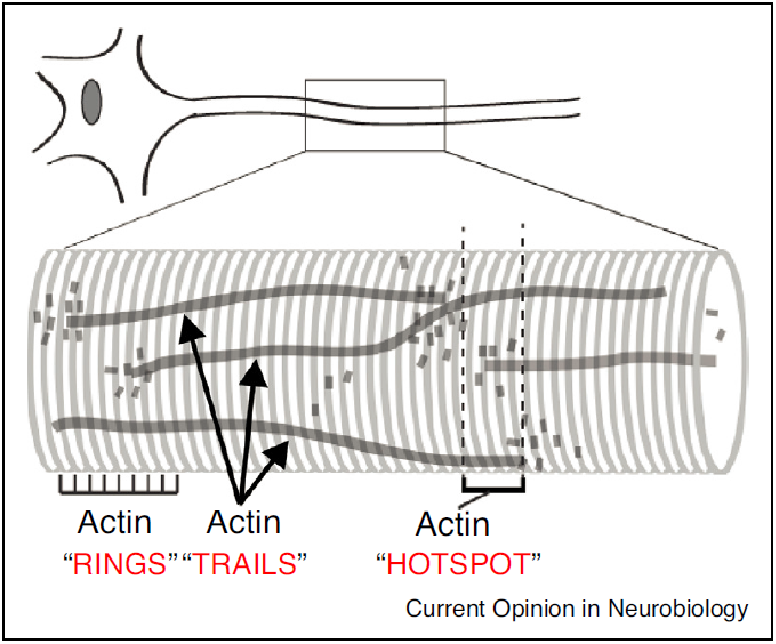
Actin Assemblies in the Axon Shaft - some Open Questions.
Current Opinion in Neurobiology 2018 Aug. Jorgenson K, Dubey P and Roy, S*. Short review of some open questions that have emerged from recent discoveries in the neuronal cytoskeleton field. Read paper here |
|
A CRISPR/Cas9 based strategy to manipulate the Alzheimer’s Amyloid Pathway. Sun J, Carlson-Stevermer J, Das U, Shen M, Wang L, Loi J, Petersen A, Stockton M, Delenclos M, McLean P, Bhattacharyya A, Jones M, Zhao X, Saha K, and Roy S*.
BioRxiv preprint server, 2018: https://www.biorxiv.org/content/early/2018/04/28/310193www.biorxiv.org/content/early/2018/04/28/310193 Story by Alzforum: https://www.alzforum.org/news/research-news/mice-crispr-based-alzheimers-therapies-inch-forward |
|
A review focused on the physical interaction of APP and BACE
|
The physical approximation of APP and BACE-1: A key event in Alzheimer's disease pathogenesis. Jichao Sun and Subhojit Roy*
Developmental Neurobiology 2018 March 78(3):340-347. doi: 10.1002/dneu.22556. Read the paper here |
2017
A comprehensive Review of the Axonal Cytoskeleton
|
The nano-architecture of the axonal cytoskeleton. Leterrier C*, Dubey P, Roy S*.
Nature Reviews in Neuroscience 2017 Nov 3. doi: 10.1038/nrn.2017.129. Read the paper here |
|
News and Views
|
Synuclein and dopamine: the Bonnie and Clyde of Parkinson’s disease. Roy S*. Nature Neuroscience 2017 Oct 26;20(11):1514-1515
Read comment here |
Chaperones helping Slow Axonal Transport

Hsc70 chaperone activity is required for the cytosolic slow axonal transport of synapsin
Ganguly A, Han X, Das U, Wang L, Loi J, Sun J, Gitler D, Caillol G, Leterrier C, Yates JR 3rd, Roy S*. Journal of Cell Biology. 2017 May Read the paper here |
|
Neuropathology in dementia with Lewy bodies
|
Hippocampal α-Synuclein in Dementia with Lewy Bodies Contributes to Memory Impairment and Is Consistent with Spread of Pathology. Adamowicz DH, Roy S, Salmon DP, Galasko DR, Hansen LA, Masliah E, Gage FH*.
Journal of Neuroscience 2017 Feb 15;37(7):1675-1684. Read this paper |
Amyloid-beta peptide is needed for cGMP-induced long-term potentiation and memory
|
|
Palmeri A, Ricciarelli R, Gulisano W, Rivera D, Rebosio C, Calcagno E, Rosaria, Tropea M, Conti S, Das U, Roy S, Pronzato MA, Arancio O, Fedele E, Puzzo D*. Amyloid-beta peptide is needed for cGMP-induced long-term potentiation and memory. J Neuroscience. 2017 Jul 19;37(29):6926-6937. PMID: 28626017
|
Commentary on work from Roy Lab (commentary)
|
Inner Workings: Uncovering the neuron’s internal skeleton - by Amber Dance, 2017 Work in the Roy lab featured in PNAS: http://www.pnas.org/content/113/49/13931 |
|
2016
Dynein's life in the slow lane (commentary)
|
Brief overview of slow axonal transport and review of Twelvetrees et al. in Neuron. Roy, S*.
Neuron. 2016 Jun 1;90(5):907-9. Read this paper |
|
A short review on axonal actin putting the bits and pieces together (review)
|
|
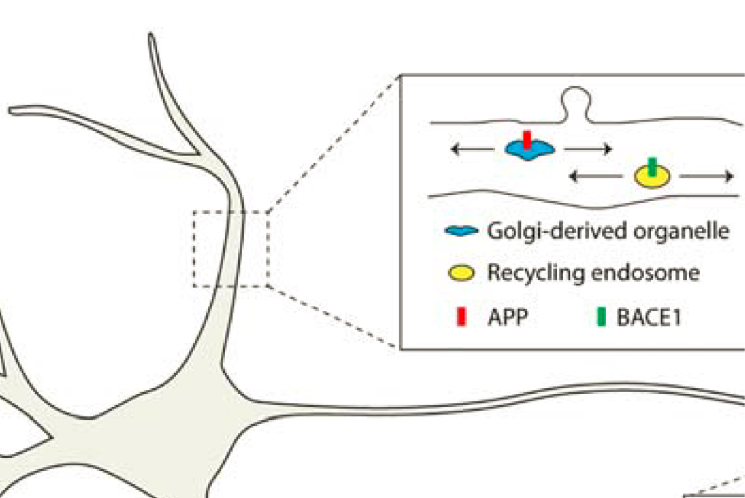
Seeing is believing: APP/BACE interactions in hippocampal neurons
|
Visualizing APP and BACE-1 approximation in neurons yields insight into the amyloidogenic pathway.
Das U, Wang L, Ganguly A, Saikia JM, Wagner SL, Koo EH, Roy S*. Nature Neuroscience. Jan 2016. doi: 10.1038/nn.4188. Read this paper |
|
2015
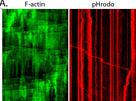
See the Whacky World of Axonal Actin....
|
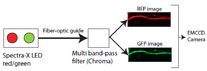
Bizarre actin dynamics in axons revealed by live imaging of F-actin and superresolution imaging. Axons contain 'hotspots' spaced ~ 3-4 um apart, where actin continuously assembles and dis-assembles - probably on stationary endosomes - and long actin filaments nucleate at these hotspots and spurt bidirectionally, supplying actin to synapses. No kidding.
Ganguly A, Tang Y, Wang L, Ladt K, Loi J, Dargent B, Leterrier C, and Roy S*. A dynamic formin-dependent deep F-actin network in axons. Journal of Cell Biology, July 27 issue; 210(3). (doi:10.1083/jcb.201506110) Read this paper * JCB In focus: Actin Hotspots Blaze a Trail along Axons * Cover * Highlighted in "The Year In Cell Biology" (JCB) |
|
Methods paper - accompanying the JCB article - to visualize neuronal F-actin dynamics
|
Follow the protocol and you shall see....exact steps to visualize F-actin dynamics in neurons. Book edited by Kevin Pfister
Ladt K, Ganguly A, and Roy S*. Actin in action: Imaging actin dynamics in neurons. Methods in Cell Biology. (http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/bs.mcb.2015.07.003) Read this paper |
2014
What does alpha-synuclein REALLY do? Here's our best guess....
|
Normally, alpha-synuclein exchanges between a monomer and multimer at the synapse. Multimeric alpha-synuclein assemblies bind to and cluster synaptic vesicles, restricting the recycling of the synaptic vesicle pool. This phenomenon is activity-dependent.
Wang L, Das U, Scott D, Tang Y, McLean P and Roy S*. Alpha-Synuclein multimers Cluster Synaptic Vesicles and attenuate Recycling. Current Biology, 2014 Sep 24. (14)01040-9. Read this paper * Report/peer-comments in ‘Alzforum’: Synuclein oligomers: Is Ensnareing Synaptic Vesicles their true calling? Form and function: What makes synuclein toxic? * News story: A "Frenemy" in Parkinson's takes to Crowdsourcing |
|
Some Basic Photoactivation Tools to study Axonal Transport
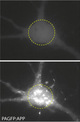
Part of a book "Photoswitching proteins - Methods and Protocols". Edited by Dr. Sidney Cambridge.
Ganguly, A* and Roy S* (2014).
Using Photoactivatable GFP to Track Axonal Transport Kinetics. Methods Mol Biol.;1148:203-15.
Read this paper
Disorganized cortical "patches" in young Autistic Brains
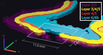
Paper from Eric Courchesne's lab showing cortical disorganization in early autistic brains. Subhojit Roy is the neuropathologist.
Stoner R, Chow ML, Boyle MP, Sunkin SM, Mouton PR, Roy S, Wynshaw-Boris A, Colamarino SA, Lein ES, Courchesne E*. (2014) Patches of disorganization in the neocortex of children with autism. N Engl J Med. 370(13):1209-19.
Read this paper
Stoner R, Chow ML, Boyle MP, Sunkin SM, Mouton PR, Roy S, Wynshaw-Boris A, Colamarino SA, Lein ES, Courchesne E*. (2014) Patches of disorganization in the neocortex of children with autism. N Engl J Med. 370(13):1209-19.
Read this paper
2013
Slow and Fast Axonal transport are linked
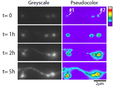
Slow axonal transport of synapsin depends upon the fast axonal transport of vesicles. A comparison of long-term kinetics of slow and fast axonal transport.
Fast vesicle transport is required for the slow axonal transport of synapsin. Tang Y, Scott D, Das U, Gitler D, Ganguly S, and Roy S*. (2013) Journal of Neuroscience, 33(39):15362-15375. * Editorial – ‘this week in the journal’ Read this paper |
Why don't we all get Alzheimer's disease?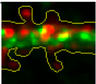
APP-cleavage by the enzyme BACE is a key event in Alzheimer’s pathology. But what prevents unabated APP-cleavage and relentless pathology? Neuronal stimulation leads to increased amyloid beta. But how does this really happen? See how APP and BACE are sorted into distinct organelles – inhibiting APP-cleavage – but converge upon triggers favoring such cleavage, such as neuronal activity.
Activity-induced convergence of APP and BACE-1 in acidic microdomains via an endocytosis-dependent pathway. Das U, Scott D, Koo EH, Tang Y and Roy S*. (2013) Neuron, 79(3):447-60. Read this paper * See ‘video abstract’ in Neuron. * Report/peer-comments in ‘Alzforum’ * News story: “Why don’t we all get Alzheimer’s disease?” – ScienceDaily, PBS, Huffington post, Scientific American - Italian, Scientific American - French |
|
Seeing the Unseen: The Hidden World of Slow Axonal Transport
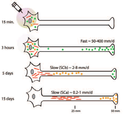
The word “axonal transport” typically invokes an image of tiny vesicles moving up and down axons – a view reinforced by ‘YouTube’ videos.
Though evocative, this is a limited portrait of axonal transport. Hidden from this picture, a deluge of cytoskeletal and soluble proteins are also moving along these very same axons, and their role in maintaining axonal and synaptic function is no less important than their vesicular counterparts. Known as slow axonal transport..........
Seeing the Unseen: the hidden world of slow axonal transport.
Subhojit Roy*, The Neuroscientist (Review) Aug 2, 2013
Read all about this mysterious phenomena here
Though evocative, this is a limited portrait of axonal transport. Hidden from this picture, a deluge of cytoskeletal and soluble proteins are also moving along these very same axons, and their role in maintaining axonal and synaptic function is no less important than their vesicular counterparts. Known as slow axonal transport..........
Seeing the Unseen: the hidden world of slow axonal transport.
Subhojit Roy*, The Neuroscientist (Review) Aug 2, 2013
Read all about this mysterious phenomena here
2012The Return of the synaptic Alpha Synuclein - When too much of a Good thing is really really bad
Alpha-synuclein inhibits inter-synaptic vesicle mobility and maintains recycling pool homeostasis.
David Scott and Subhojit Roy*. Journal of Neuroscience, 2012 July 25; 32(30):10129-35. Read this paper Data suggest that alpha-synuclein may regulate the size of recycling pool (and consequently neurotransmitter release) by regulating vesicle-trafficking between synaptic boutons. |
Check out our Cover
|
Axonal transport of alpha-synuclein
The slow axonal transport of alpha-synuclein – mechanistic commonalities amongst diverse cytosolic cargoes.
Yong Tang, Utpal Das (co-first authors), David Scott and Subhojit Roy*. Cytoskeleton (special issue on South American cell biology meeting), Jul;69(7):506-13. 2012. Read this paper Employs our new technique to study the slow axonal transport of alpha-synuclein. |
Check out our Cover
Imaginary view of Fast and Slow Axonal Transport
|
Effects of amyloid-beta on axonal transport - what's the mechanism?
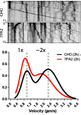
Early and selective impairments in axonal transport kinetics of synaptic cargoes induced by soluble amyloid beta-protein oligomers.
Yong Tang, David Scott, Utpal Das, Steven Edland, Kryslaine Radomski, Edward H. Koo and Subhojit Roy* Traffic. May 2012;13(5):681-93
Read this paper
Describes early effects of soluble, cell-derived amyloid-beta oligomers (200 picomolar!) on axonal transport of various vesicular cargoes imaged under controlled, standardized protocols. The effects are selective (only synaptic cargoes are affected; no effects on mitochondrial motility), executed via an NMDA-receptor/GSK3b - mediated pathway, and may result from diminished cargo/motor engagement.
Yong Tang, David Scott, Utpal Das, Steven Edland, Kryslaine Radomski, Edward H. Koo and Subhojit Roy* Traffic. May 2012;13(5):681-93
Read this paper
Describes early effects of soluble, cell-derived amyloid-beta oligomers (200 picomolar!) on axonal transport of various vesicular cargoes imaged under controlled, standardized protocols. The effects are selective (only synaptic cargoes are affected; no effects on mitochondrial motility), executed via an NMDA-receptor/GSK3b - mediated pathway, and may result from diminished cargo/motor engagement.
Harnessing the power of photoactivatable probes to study axonal transport - Try this at home!
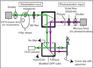
A simple photoactivation and image-analysis module for visualizing and analyzing axonal transport with high temporal resolution.
Subhojit Roy*, Ge Yang, Yong Tang, and David Scott. Nature Protocols, January 2012 issue. Read this paper
Describes a simple add-on that can be retroactively fitted on an epifluorescence (Olympus) microscope to evaluate axonal transport of cargoes tagged to photoactivatable probes with high temporal resolution. A relatively low-cost option that can even be used for analyzing proteins with very fast diffusible pools, with no compromise in data-quality. Image-analyses procedures and experimental caveats/troubleshooting tips are also provided.
Subhojit Roy*, Ge Yang, Yong Tang, and David Scott. Nature Protocols, January 2012 issue. Read this paper
Describes a simple add-on that can be retroactively fitted on an epifluorescence (Olympus) microscope to evaluate axonal transport of cargoes tagged to photoactivatable probes with high temporal resolution. A relatively low-cost option that can even be used for analyzing proteins with very fast diffusible pools, with no compromise in data-quality. Image-analyses procedures and experimental caveats/troubleshooting tips are also provided.
2011
The logic of slow axonal transport: How does the soluble protein move anyway?
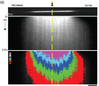
Mechanistic logic underlying the axonal transport of cytosolic proteins.
David Scott, Utpal Das (co-first authors), Yong Tang and Subhojit Roy*. Neuron May 2011 12;70(3):441-54. Describes a new way by which cytosolic proteins may be transported. Read this paper
* See Preview: "The Curious Case of the Soluble Protein". Scott T. Brady. Dev Cell. 2011 May 17;20(5):581-2. Read this Preview
* See UCSD News story: “Slow Road to the Synapse: Why some proteins take their time getting there.”
David Scott, Utpal Das (co-first authors), Yong Tang and Subhojit Roy*. Neuron May 2011 12;70(3):441-54. Describes a new way by which cytosolic proteins may be transported. Read this paper
* See Preview: "The Curious Case of the Soluble Protein". Scott T. Brady. Dev Cell. 2011 May 17;20(5):581-2. Read this Preview
* See UCSD News story: “Slow Road to the Synapse: Why some proteins take their time getting there.”
A Simulated Biopsy paradigm to hypothetically diagnose neurodegenerative diseases - A Neuropathologic study
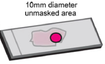
Simulated brain biopsy for diagnosing neurodegeneration using autopsy-confirmed cases. Venneti S, Robinson JL, Roy S, White MT, Baccon J, Xie SX, Trojanowski JQ*. Acta Neuropathol. 2011 Dec;122(6):737-45. Read this paper
2010 and before
Alpha-synuclein at the synapse: What makes a perfectly good synapse go Boink?
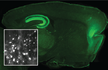
A pathologic cascade leading to synaptic dysfunction in α-synuclein-induced neurodegeneration.
David Scott, Iustin Tabarean, Yong Tang, Anna Cartier, Eliezer Masliah and Subhojit Roy*.
Journal of Neuroscience Jun 2010 16;30(24):8083-95. Read this paper
Describes the development of a new model-system by which evolvng alpha-synuclein pathology can be quantitatively assessed in neurons.
* Editorial comment in “This week in the journal” Link to Pubmed
* UCSD News story: UCSD: News
* See report/peer-comments on the online community Alzforum: Alzforum: News
David Scott, Iustin Tabarean, Yong Tang, Anna Cartier, Eliezer Masliah and Subhojit Roy*.
Journal of Neuroscience Jun 2010 16;30(24):8083-95. Read this paper
Describes the development of a new model-system by which evolvng alpha-synuclein pathology can be quantitatively assessed in neurons.
* Editorial comment in “This week in the journal” Link to Pubmed
* UCSD News story: UCSD: News
* See report/peer-comments on the online community Alzforum: Alzforum: News
Review on axonal transport and neurodegenerative diseases
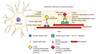
Axonal transport and neurodegenerative diseases (Review). Subhojit Roy, Virginia Lee and John Q. Trojanowski.
Encyclopedia of Neuroscience (2009), vol. 1, pp. 1199-1203.
A review of links between axonal transport and neurodegeneration. Read this paper
Encyclopedia of Neuroscience (2009), vol. 1, pp. 1199-1203.
A review of links between axonal transport and neurodegeneration. Read this paper
The paradox of alpha-synuclein
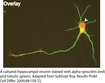
The paradoxical cell biology of α-synuclein. Roy S*, Results Probl Cell Differ. 2009;48:159-72.
Alpha-synuclein is a small, soluble protein that normally localizes to the presynaptic terminals. Yet in diseased states, large amounts of alpha-synuclein is found within cell bodies and proximal neurons. This review considers the hypothesis that the axonal transport and presynaptic targeting of the protein is disturbed in diseased states. Read this paper
Alpha-synuclein is a small, soluble protein that normally localizes to the presynaptic terminals. Yet in diseased states, large amounts of alpha-synuclein is found within cell bodies and proximal neurons. This review considers the hypothesis that the axonal transport and presynaptic targeting of the protein is disturbed in diseased states. Read this paper
2008 and Before
Alpha-synuclein induces curious vesicular accumulations in the yeast
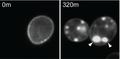
α-synuclein Induced Aggregation of Cytoplasmic Vesicles in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. James Soper, Subhojit Roy, Anna Steiber, Chris Burd, Virginia Lee.
Molecular Biology of the Cell. Jan 2008 19(3), 1093-1103.
Curious vesicular accumulations upon alpha-synuclein over-expression in yeast. Is this an artifact, or is mother nature trying to tell us something? Make up your own mind, Read this paper
Molecular Biology of the Cell. Jan 2008 19(3), 1093-1103.
Curious vesicular accumulations upon alpha-synuclein over-expression in yeast. Is this an artifact, or is mother nature trying to tell us something? Make up your own mind, Read this paper
Role of f-actin on transport of cytosolic cargoes
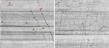
Cytoskeletal requirements of Slow Component-b transport. Subhojit Roy, Matthew J. Winton, Mark M. Black, John Q. Trojanowski, Virginia Lee.
Journal of Neuroscience May 2008 28(20):5248-5256. Read this paper
Journal of Neuroscience May 2008 28(20):5248-5256. Read this paper
Co-transport of cytosolic cargoes
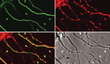
Rapid and intermittent co-transport of Slow Component-b proteins. Subhojit Roy, Matthew J. Winton, Mark M. Black, John Q. Trojanowski, Virginia Lee.
Journal of Neuroscience Mar 2007 27(12):3131-38. Read this paper
* Featured with editorial comment in “This week in the journal”
Journal of Neuroscience Mar 2007 27(12):3131-38. Read this paper
* Featured with editorial comment in “This week in the journal”
Axonal transport of neurofilament polymers: The one that started it all
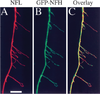
Neurofilaments are Transported Rapidly but Intermittently in Axons: Implications for Slow Axonal Transport. Subhojit Roy, Pilar Coffee, George Smith, Ron K. Liem, Scott T. Brady and Mark M. Black.
Journal of Neuroscience Sept 2000; 20(18):6849-6861. Read this paper
Subhojit Roy's PhD thesis!
Journal of Neuroscience Sept 2000; 20(18):6849-6861. Read this paper
Subhojit Roy's PhD thesis!